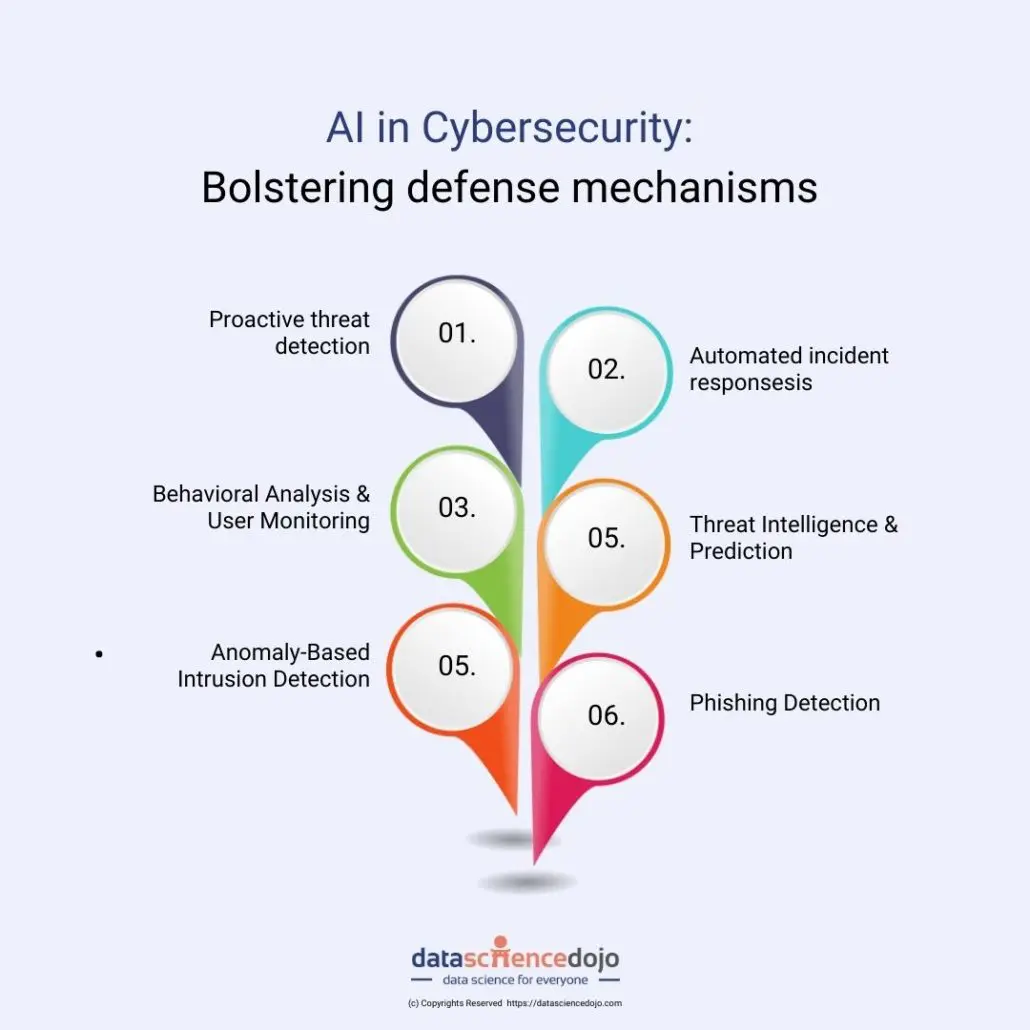
As technology continues to evolve at breakneck speed, the threats lurking in the digital world have grown more complex and dangerous. Traditional cybersecurity tools—based on static rules and human oversight—are no longer sufficient to combat sophisticated cyberattacks. In response, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a revolutionary force in cybersecurity, enabling organizations to detect, prevent, and respond to threats with unprecedented speed and precision.
AI-driven cybersecurity offers real-time threat monitoring, adaptive defenses, and automated incident response. It’s not just an improvement—it’s a complete transformation of how we defend digital infrastructure. In this comprehensive article, we explore the inner workings, applications, benefits, challenges, and future of AI in cybersecurity.
Understanding AI in Cybersecurity
AI in cybersecurity refers to the use of algorithms, machine learning models, and intelligent automation to protect networks, systems, and data from malicious activities. It includes tools and techniques designed to simulate human intelligence while working far faster and across larger datasets.
Key Components:
A. Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms trained on large volumes of data to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential threats.
B. Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems that understand and analyze human language, useful in scanning phishing emails and social engineering attempts.
C. Neural Networks: Deep learning models that process vast data streams to detect complex threats, such as zero-day exploits.
D. Behavioral Analysis: AI that creates baselines of normal user or network behavior and flags deviations that may indicate threats.
How AI Cybersecurity Works
AI-powered security systems constantly scan massive amounts of data to identify threats in real time. Unlike traditional methods, which rely on known threat signatures, AI can recognize previously unseen threats by understanding behavior and context.
Core Functions:
A. Threat Detection: AI identifies unusual patterns in system or network activity that could signal an attack.
B. Threat Prediction: Using historical data, AI forecasts potential future threats and vulnerabilities.
C. Automated Response: AI can isolate systems, cut off access, or trigger countermeasures without human intervention.
D. Threat Hunting: AI assists security analysts in investigating and analyzing potential threats.
Major Applications of AI in Cybersecurity
AI is being deployed across a wide range of cybersecurity domains, including:
A. Malware Detection
AI can detect and block malware based on behavior, even if the specific malware strain has never been seen before. Traditional antivirus software relies on signature databases, which are ineffective against new or altered threats.
B. Phishing Attack Prevention
With NLP, AI can analyze emails and messages to identify phishing attempts. It detects subtle signs—like tone, sender inconsistencies, or suspicious links—often missed by users.
C. Network Intrusion Detection
AI continuously monitors network traffic, alerting security teams of irregularities or breaches in real time. It can identify advanced persistent threats (APTs) that dwell inside systems for extended periods.
D. Endpoint Security
AI secures devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets by detecting unauthorized access attempts, suspicious file downloads, or application behavior.
E. Fraud Detection
Financial institutions use AI to identify irregular transactions, credit card fraud, and identity theft attempts with remarkable accuracy.
F. Insider Threat Management
By monitoring user behavior, AI can detect when an employee or contractor is behaving suspiciously—possibly indicating sabotage, data theft, or misuse.
G. Vulnerability Management
AI continuously scans systems for known vulnerabilities, prioritizes patching based on risk levels, and even recommends or applies fixes automatically.
Benefits of AI-Powered Cybersecurity

Adopting AI in cybersecurity brings a multitude of advantages:
A. Speed and Scale
AI processes terabytes of data in real time, enabling organizations to detect threats faster than human analysts ever could.
B. Reduced False Positives
AI improves accuracy by learning over time, reducing the number of false alerts and allowing teams to focus on real threats.
C. Adaptive Learning
AI evolves with the threat landscape, improving as it encounters new threats, tactics, and vulnerabilities.
D. Proactive Defense
Instead of waiting for an attack to occur, AI can predict and prevent breaches before they happen.
E. Automation of Repetitive Tasks
Routine security operations such as log analysis and event correlation can be automated, freeing up human analysts for critical work.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Cybersecurity
Despite its potential, AI-driven cybersecurity is not without challenges:
A. Data Dependency
AI systems need massive amounts of clean, structured data to train effectively. Poor-quality data can lead to flawed models.
B. High Costs
Implementing AI cybersecurity solutions can be expensive, requiring investment in infrastructure, talent, and software.
C. Model Bias
AI systems can reflect the biases of their training data, possibly overlooking threats or falsely flagging benign activity.
D. Adversarial Attacks
Hackers may try to trick AI systems using adversarial inputs—specially crafted data that causes the model to misclassify or ignore threats.
E. Over-Reliance
Too much dependence on AI can create blind spots if human oversight is eliminated. A hybrid model with AI-human collaboration is essential.
AI vs. Traditional Cybersecurity
| Feature | Traditional Cybersecurity | AI-Driven Cybersecurity |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Signature-based | Behavior-based |
| Response Time | Reactive | Real-time or proactive |
| Scalability | Manual limitations | High scalability |
| Human Involvement | High | Moderate to low |
| Threat Coverage | Known threats only | Known and unknown threats |
AI is not a replacement for traditional tools but a powerful enhancement that makes cybersecurity more dynamic and robust.
Real-World Examples
A. Darktrace
This cybersecurity firm uses self-learning AI to detect and respond to cyber threats in real time. It analyzes normal behavior and identifies deviations across networks, cloud, and email systems.
B. IBM Watson for Cybersecurity
IBM’s AI platform applies NLP and machine learning to assist security analysts with investigations and threat hunting.
C. Microsoft Defender
Microsoft’s cybersecurity platform integrates AI to detect malware, ransomware, and phishing attempts across Windows, cloud services, and Microsoft 365.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
The coming years will bring even more sophisticated AI systems, making cyber defense stronger—but also raising the stakes for attackers.
Emerging Trends:
A. Explainable AI (XAI): Systems that not only make decisions but explain them, increasing trust and transparency.
B. Federated Learning: AI that trains across multiple decentralized devices while preserving privacy.
C. AI-Powered DevSecOps: Integrating AI into the development pipeline for secure-by-design applications.
D. Collaborative Defense Platforms: AI systems that share threat intelligence across companies and sectors in real time.
E. Quantum-Resilient AI: Preparing for the post-quantum era with AI tools that defend against quantum-computing threats.
How to Implement AI Cybersecurity in Your Organization
For businesses looking to integrate AI in their security architecture, consider the following steps:
A. Assess Needs and Gaps: Identify which areas of your current security setup are vulnerable or inefficient.
B. Choose the Right Tools: Select AI solutions that align with your infrastructure and threat landscape.
C. Invest in Training: Ensure IT and security personnel understand how to work alongside AI systems.
D. Monitor and Fine-Tune Models: Continuously evaluate AI performance and adjust based on real-world feedback.
E. Maintain Human Oversight: Use AI as a force multiplier, not a full replacement for expert judgment.
Conclusion: AI Is the Future of Cyber Defense
AI is reshaping cybersecurity from a passive, reactive discipline into a proactive, intelligent, and dynamic field. While there are valid concerns and limitations, the benefits—speed, accuracy, scalability, and automation—are too significant to ignore.
Organizations that embrace AI will be better equipped to deal with tomorrow’s cyber threats today. Whether you’re a startup or a multinational enterprise, integrating AI into your security strategy is not just smart—it’s essential.